The world of electricity is constantly evolving, driven by the need to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
One of the key techniques for optimising electricity distribution is power factor correction. This process plays a crucial role in ensuring that electrical systems operate efficiently and reliably.
In this article, we will explore power factor correction calculation in detail, highlighting its importance and the methodologies involved in electricity optimisation.
What is power factor correction
Power factor correction is the process of adding reactive components to an electrical system in order to compensate for reactive power and improve the power factor. Reactive power is that part of the energy not actually used to perform useful work. It can cause energy losses, overheating of cables and other problems in the electrical system.
Power factor correction calculation helps address these inefficiencies by determining the right compensation strategy to optimise system performance.
How power factor correction works
Power factor correction exploits the use of reactive components, such as capacitors, which can store and release reactive energy in order to balance the reactive power in the system. This process reduces energy losses, improves the stability of the electrical system and extends the life of equipment. A precise power factor correction calculation is essential to ensure that the installed compensation matches the actual needs of the system.
Power factor correction methods: choosing the right solution
There are several methods for implementing power factor correction, including:
- Centralised compensation: consists of installing power factor correction in such a way that it works for the whole system.
- Distributed Compensation: consists of installing capacitor banks directly on individual loads, such as motors or transformers, improving local efficiency.
- Fixed Compensation: suitable for constant loads, involves the installation of fixed capacitors sized according to the load.
- Automatic Compensation: ideal for variable loads, it uses capacitor banks that are automatically switched on or off according to the needs of the system.
The choice of the most appropriate method depends on the specific characteristics of the system and its load profiles.
The power factor correction calculation
Power factor correction calculation is a process that requires detailed knowledge of the characteristics of the electrical system.
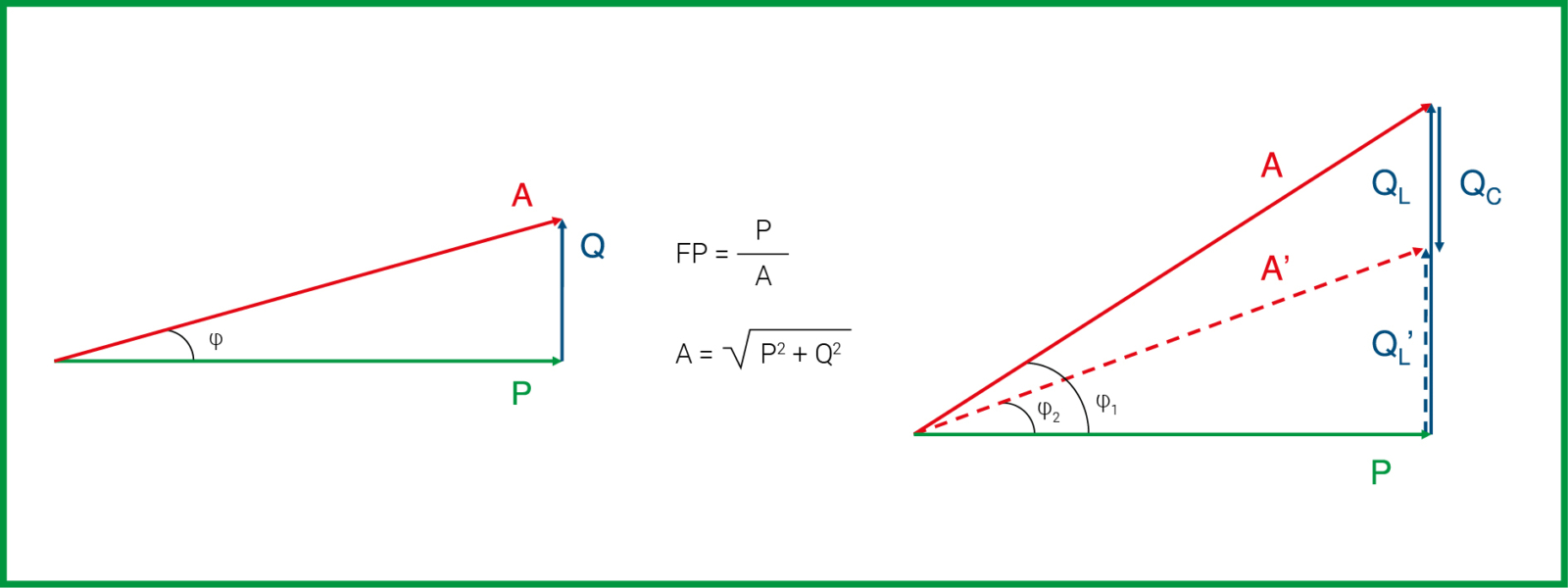
Reactive power is one of the main variables to be considered. To calculate it, it is necessary to know the apparent power, which is the combination of active and reactive power. The latter can be calculated as the square root of the apparent power squared minus the active power squared.
Once the reactive power has been obtained, the dimensioning of the reactive components required for effective power factor correction can be determined.
Here’s how the power factor correction calculation works in detail:
The choice of capacitor bank to be installed in a system is directly dependent on:
- the cosφ2 value to be obtained
- starting cosφ1 value
- installed active power
To determine the reactive power (QC) required for power factor correction, the formula is used:
QC = P x (tanφ1 – tanφ2)
Where tanφ1 and tanφ2 are the tangents of the initial and desired phase shift angles.
This calculation allows the capacitor bank required to achieve the desired power factor to be correctly dimensioned.
The benefits on your electricity bill
The benefits of power factor correction are manifold. Firstly, it improves energy efficiency by reducing energy losses caused by excess reactive power.
It avoids bill penalties that are imposed by energy distribution companies in many countries.
This not only saves money, but also reduces the environmental impact.
In addition, power factor correction increases the lifetime of electrical equipment, as it reduces wear and tear due to reactive energy fluctuations.
Try our Power Factor Correction Calculator
Need help with your power factor correction calculation?
Ortea Next offers a free and easy-to-use Power Factor Correction Calculator to support technicians, engineers and energy managers in dimensioning reactive power compensation systems. Just enter your system parameters to instantly receive tailored suggestions for optimising power factor and improving energy efficiency.
In a world increasingly focused on efficiency and sustainability, power factor correction calculation emerges as an important tool in electricity optimisation. The ability to balance reactive power through the addition of reactive components offers tangible benefits in both economic and environmental terms. Understanding power factor correction calculation and its implementation not only improves energy management, but also contributes to the creation of more stable and reliable electrical systems, promoting a sustainable energy future.